Jaundice in dogs can be a serious condition that requires prompt veterinary attention. However, there are several home treatments that can help alleviate the symptoms and support the dog’s liver function while under veterinary care. Home treatments for jaundice dogs may include dietary changes, liver support supplements, hydration, monitoring of glucose and electrolyte levels, avoiding exposure to toxins, physical activity, and even herbal remedies. It is important to note that these treatments should always be done under the supervision of a veterinarian, as certain conditions may require more aggressive medical intervention. In this article, we will explore the most important home treatments for jaundice dogs and how they can support the dog’s recovery.
Table of Contents
ToggleWhat is jaundice in dogs?
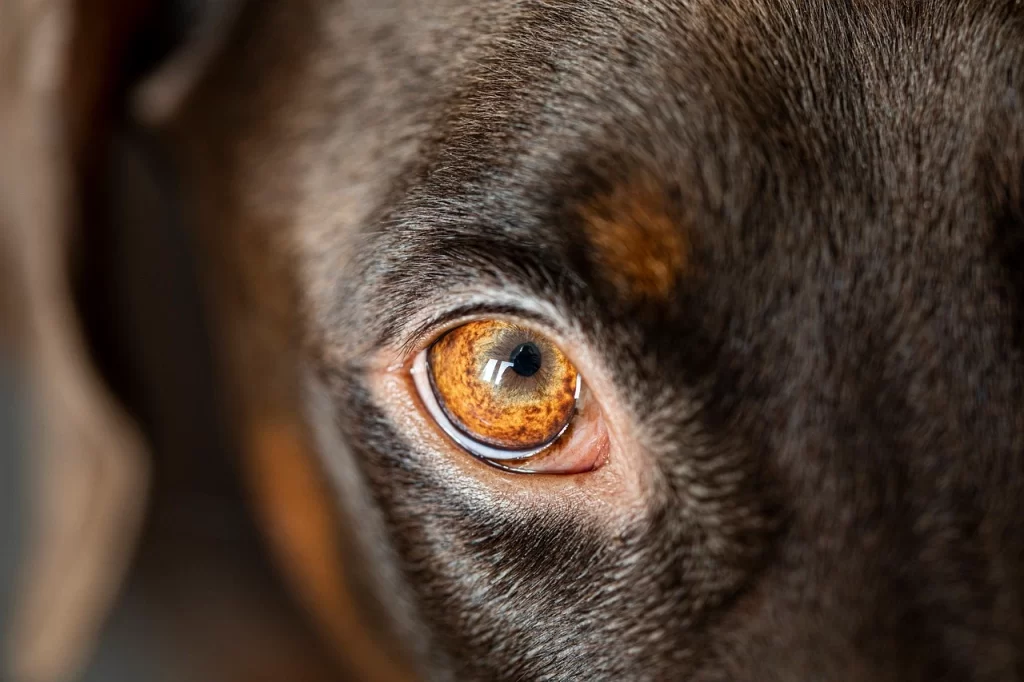
Jaundice in dogs (also known as Icterus in dogs) is a condition characterized by a yellowing of the skin, gums, and whites of the eyes. This yellowing is caused by an excess of bilirubin, a yellow pigment, in the blood. Bilirubin is produced when red blood cells break down and are normally processed by the liver and excreted from the body. When the liver is not functioning properly, bilirubin accumulates in the blood and causes jaundice.
Jaundice in dogs can be a sign of liver disease, infection, or a number of other underlying health conditions. In some cases, jaundice can be a symptom of a serious, life-threatening condition and prompt veterinary care is necessary. Jaundice can also be caused by medication or exposure to toxins. Regardless of the cause, it is important to address jaundice as soon as possible in order to improve the chances of a successful outcome. In severe cases, a liver transplant may be necessary to save a dog’s life. Early detection and treatment is key to managing jaundice in dogs and promoting a successful recovery.
Causes of jaundice in dogs
Jaundice in dogs is caused by an excess of bilirubin in the bloodstream. Bilirubin is a yellow pigment that is produced when red blood cells break down. Normally, the liver processes bilirubin and excretes it from the body. However, when the liver is not functioning properly, bilirubin accumulates in the bloodstream and causes jaundice. There are several underlying health conditions that can cause jaundice in dogs, including:
- Liver Disease: The liver is responsible for processing bilirubin and excreting it from the body. When the liver is diseased, it may not function properly, leading to the accumulation of bilirubin in the blood and jaundice. Examples of liver diseases that can cause jaundice in dogs include hepatitis, liver tumors, and liver shunts.
- Hemolytic Anemia: Hemolytic anemia is a condition in which red blood cells are destroyed faster than they can be produced, leading to anemia and jaundice. Hemolytic anemia can be caused by autoimmune disorders, infections, toxins, or certain medications.
- Parasites: Parasites, such as hookworms, can cause jaundice in dogs by destroying red blood cells and causing anemia.
- Pancreatitis: Pancreatitis is inflammation of the pancreas that can cause jaundice in dogs by interfering with the normal processing of bilirubin.
- Toxins: Exposure to toxins, such as certain plants, insecticides, and medications, can cause jaundice in dogs.
- Cancer: Certain cancers, such as lymphoma and leukemia, can cause jaundice in dogs by interfering with the normal processing of bilirubin.
- Infections: Infections, such as leptospirosis, can cause jaundice in dogs by damaging the liver and interfering with the normal processing of bilirubin.
- Trauma: Traumatic injury, such as a car accident, can cause jaundice in dogs by damaging the liver and other organs.
Note that jaundice can be a sign of a serious underlying health condition, and prompt veterinary care is necessary to diagnose and treat the underlying cause.
Symptoms of jaundice in dogs
The symptoms of jaundice in dogs can vary depending on the underlying cause, but common symptoms include yellowing of the skin, gums, and whites of the eyes. Other symptoms can include:
- Loss of appetite
- Fatigue and weakness
- Vomiting and diarrhea
- Abdominal pain and swelling
- Dehydration
- Increased thirst and urination
- Changes in behavior, such as confusion and disorientation
- Jaundice may also be accompanied by symptoms related to the underlying cause, such as fever (in case of infections), increased drinking and urination (in case of liver disease), or sudden collapse (in case of Hemolytic Anemia).
Seek veterinary care if you suspect your dog may have jaundice, as prompt treatment can improve the chances of a successful outcome. The veterinarian will perform a thorough physical examination, including a blood test to assess liver function and confirm the presence of jaundice.
Diagnosing jaundice in dogs
The diagnosis of jaundice in dogs involves a thorough physical examination, including a blood test to assess liver function and confirm the presence of jaundice. Depending on the underlying cause of jaundice, additional diagnostic tests may be necessary to determine the cause and develop an appropriate treatment plan. Some of these tests include:
- Complete Blood Count (CBC): A CBC can help to determine if there is anemia, which may indicate hemolytic anemia.
- Blood Chemistry Panel: A blood chemistry panel can evaluate the function of the liver and other organs and provide information on electrolyte and glucose levels, which can be disrupted in liver disease and other underlying causes of jaundice.
- Urinalysis: A urinalysis can help to assess kidney function and detect any signs of infection, which may indicate leptospirosis or other infections.
- Fecal Examination: A fecal examination can detect parasites, such as hookworms, which can cause jaundice.
- Abdominal Ultrasound: An abdominal ultrasound can help to visualize the liver and other organs and detect any abnormalities, such as tumors or shunts, which can cause jaundice.
- Biopsy: A biopsy of the liver or other affected organs may be necessary to diagnose liver disease, tumors, or other underlying causes of jaundice.
- Serology Tests: Serology tests, such as antibody tests, can help to diagnose infections, such as leptospirosis.
- Specialized Tests: Depending on the suspected underlying cause of jaundice, additional specialized tests, such as toxin screenings, may be necessary.
Remember that a correct diagnosis is essential for the development of an appropriate treatment plan, so it’s important to seek veterinary care if you suspect your dog may have jaundice.
Risk factors and potential complications
The risk factors for jaundice in dogs vary depending on the underlying cause, but some common risk factors include:
- Age: Older dogs are more susceptible to liver disease and other conditions that can cause jaundice.
- Breed: Certain breeds, such as Cocker Spaniels and English Springer Spaniels, are predisposed to certain liver diseases that can cause jaundice.
- Environmental exposures: Exposure to toxins, such as certain medications or household chemicals, can increase the risk of jaundice in dogs.
- Infections: Infections, such as leptospirosis, can cause jaundice in dogs.
Potential complications of jaundice in dogs, with or without treatment, can include:
- Liver Failure: If the underlying cause of jaundice is liver disease, untreated jaundice can lead to liver failure, which can be life-threatening.
- Spread of Infection: If the underlying cause of jaundice is an infection, the infection can spread to other parts of the body, leading to further complications.
- Anemia: If the underlying cause of jaundice is hemolytic anemia, the red blood cells may continue to break down, leading to anemia and further complications.
- Tissue Damage: If jaundice is left untreated, it can lead to tissue damage in the liver and other organs, which can be irreversible.
Survival rates jaundiced dogs
The survival rate for dogs with jaundice depends on several factors, including the underlying cause of jaundice, the severity of the condition, and the promptness of treatment. Here are some general survival rate estimates for different cases or options:
- Acute liver disease: If jaundice is caused by acute liver diseases, such as toxic liver disease or viral hepatitis, the survival rate is generally good with prompt treatment. With supportive care, antibiotics, and medications to improve liver function, many dogs can recover completely.
- Chronic liver disease: If jaundice is caused by chronic liver disease, such as liver cirrhosis, the survival rate is lower, but the prognosis can still be good with appropriate treatment. Treatment options may include dietary changes, medications, and supplements to support liver function, but the response to treatment can vary.
- Hemolytic anemia: If jaundice is caused by hemolytic anemia, the survival rate depends on the severity of the anemia and the underlying cause. With prompt and appropriate treatment, many dogs can recover from hemolytic anemia and jaundice.
- Cancer: If jaundice is caused by cancer, such as liver or spleen tumors, the survival rate depends on the type of cancer and the stage of the disease. With prompt and appropriate treatment, including surgery, chemotherapy, or radiation therapy, some dogs can achieve long-term remission.
- Infections: If jaundice is caused by an infection, such as leptospirosis, the survival rate depends on the severity of the infection and the promptness of treatment. With appropriate antibiotics and supportive care, many dogs can recover from jaundice caused by infections.
Here are 10 of the most important home treatments for jaundice in dogs:
- Diet modification: Providing a balanced, low-fat diet can help support liver function and reduce the strain on the liver.
- Hydration: Providing plenty of fresh water and encouraging your dog to drink can help flush toxins from the body and support liver function.
- Avoidance of toxins: Avoid exposing your dog to any known toxins, such as certain medications or household chemicals.
- Supplements: Certain supplements, such as milk thistle and s-adenosylmethionine (SAMe), can help support liver function and reduce liver inflammation.
- Increased activity: Encouraging your dog to be more active, such as taking short walks or playing with toys, can help improve blood flow and liver function.
- Reduced stress: Reducing stress can help improve liver function and reduce the risk of liver disease.
- Avoidance of fasting: Avoid fasting your dog for extended periods, as this can increase the strain on the liver.
- Regular check-ups: Regular check-ups with your veterinarian can help detect and treat jaundice and other health issues early on.
- Management of underlying conditions: Treating any underlying conditions, such as infections or diabetes, can help improve liver function and reduce the risk of jaundice.
- Supportive care: Providing supportive care, such as ensuring your dog is comfortable and pain-free, can help improve the quality of life for dogs with jaundice.
- Vitamin therapy: Vitamin therapy, such as providing B-complex vitamins and vitamin C, can help support liver function and reduce oxidative stress.
- Probiotics: Providing probiotics can help support gut health and improve liver function by reducing inflammation.
- Omega-3 fatty acids: Omega-3 fatty acids, such as those found in fish oil, can help reduce inflammation and improve liver function.
- Limited protein: Limiting protein in your dog’s diet can help reduce the strain on the liver and improve liver function.
- Anti-nausea medication: Anti-nausea medication can help reduce nausea and vomiting, which can improve the quality of life for dogs with jaundice
The importance of diet and hydration in jaundiced dogs
Diet and hydration play a crucial role in supporting liver function and reducing the strain on the liver in jaundiced dogs.
A balanced and low-fat diet is essential for jaundiced dogs to support liver function. Your veterinarian may recommend a prescription diet or you can prepare a home-cooked meal with ingredients like lean proteins (such as chicken, fish, or turkey), complex carbohydrates (such as brown rice, sweet potatoes, or whole grains), and healthy fats (such as olive oil, flaxseed oil, or coconut oil). It’s important to limit high-fat foods and protein to reduce the stress on the liver.
Proper hydration is also crucial for jaundiced dogs. Make sure your dog has access to plenty of fresh water at all times. To encourage drinking, you can place several water bowls around the house, add low-sodium broth to the water, or use a water fountain. You can also freeze low-sodium broth into ice cubes and use them as treats.
It’s essential to work with your veterinarian to develop a tailored diet and hydration plan for your jaundiced dog, as every case is unique and may require individualized recommendations. Changes to your dog’s diet and hydration should only be made under veterinary supervision to ensure their health and well-being.
Liver support supplements for jaundiced dogs
Liver support supplements can play a crucial role in supporting liver function in jaundiced dogs. However, it’s important to note that these supplements should only be used under the guidance of a veterinarian. Here is a list of common liver support supplements, along with usage instructions:
- S-Adenosylmethionine (SAMe): SAMe is a naturally occurring substance that helps support liver function and improve liver health. It is typically given orally.
- Milk Thistle: Milk thistle is an herb that is commonly used to support liver function. It is typically given orally in the form of a supplement or tincture.
- Vitamin E: Vitamin E is an antioxidant that can help protect the liver from damage. It is typically given orally in the form of a supplement.
- N-Acetyl Cysteine (NAC): NAC is an amino acid that helps support liver function and can help reduce oxidative stress on the liver. It is typically given orally in the form of a supplement.
- Vitamin K: Vitamin K can help support liver function and can be used to reduce bleeding caused by liver disease. It is typically given orally in the form of a supplement.
Medications for treating jaundice in dogs
Medication can play an important role in treating jaundice in dogs, but it should only be used under the guidance of a veterinarian. There are several available medical treatments, including both prescription and over-the-counter medicines, that can be used to address underlying causes of jaundice and support liver function.
- Prescription Medications: Depending on the underlying cause of jaundice, a veterinarian may prescribe specific medications to help address the problem. For example, if the jaundice is caused by liver disease, a veterinarian may prescribe medications to help support liver function and reduce inflammation.
- Antibiotics: If an infection is causing jaundice, a veterinarian may prescribe antibiotics to help clear the infection.
- Corticosteroids: Corticosteroids can help reduce inflammation and support liver function. They may be prescribed if the jaundice is caused by liver disease.
- Over-the-Counter Medications: There are several over-the-counter medications that can help support liver function and reduce oxidative stress on the liver. These include milk thistle, s-adenosylmethionine (SAMe), and N-acetyl cysteine (NAC).
It’s important to note that not all over-the-counter medications are safe for dogs, and some may even be harmful.
Avoiding fasting: An essential in jaundice treatment for dogs
Fasting can be detrimental for dogs suffering from jaundice as it can put additional stress on the liver. When the liver is not functioning properly, it needs a constant supply of nutrients to help with the healing process. Fasting can cause a further decline in liver function and worsen the jaundice symptoms.
It’s important to provide small, frequent meals to a jaundiced dog instead of fasting. A well-balanced, nutrient-rich diet can help support liver function and provide the necessary energy to help the dog’s body heal. A veterinarian can help recommend a diet plan that is best suited for the individual dog’s needs.
It’s also essential to keep the dog hydrated by providing fresh, clean water at all times. Encouraging the dog to drink by adding flavor to the water or offering ice cubes can help increase fluid intake and prevent dehydration. In severe cases, fluid therapy may be necessary to help support liver function and prevent dehydration.
Why monitoring glucose levels is important?
Monitoring glucose levels is important in jaundiced dogs because high levels of glucose can put additional stress on the liver. The liver is responsible for regulating glucose levels in the body, and when the liver is not functioning properly, glucose levels can become elevated.
High glucose levels can contribute to liver damage and worsen jaundice symptoms. To prevent this, it’s important to monitor glucose levels in jaundiced dogs and provide treatment if necessary. A veterinarian may recommend a glucose-lowering medication or dietary changes to help regulate glucose levels.
It’s also important to monitor the dog’s overall health, including eating habits, weight, and energy levels, as changes in these areas can indicate changes in glucose levels.
There are several ways to measure glucose levels at home in dogs:
- Glucose meter: A glucose meter is a device that measures glucose levels in a small sample of blood. A drop of blood is obtained from the dog’s ear or paw, and the meter gives a reading of the glucose level.
- Glucose test strips: Test strips are used in conjunction with a glucose meter to measure glucose levels. The test strip is placed in the meter, and a drop of blood is applied to the strip, which then gives a reading of the glucose level.
- Continuous glucose monitoring (CGM) system: A continuous glucose monitoring system is a device that measures glucose levels in real time and provides constant updates on the dog’s glucose levels.
Electrolyte monitoring in jaundiced dogs: Why it matters
Monitoring electrolyte levels is important in jaundiced dogs because imbalances can occur when the liver is not functioning properly. Electrolytes, such as sodium, potassium, and calcium, are important for maintaining proper fluid balance, transmitting nerve impulses, and contracting muscles.
There are several ways to measure electrolyte levels in dogs:
- Blood test: A blood test is the most accurate way to measure electrolyte levels. A sample of blood is taken from the dog and sent to a laboratory for analysis.
- Urine test: A urine test can provide information about electrolyte levels but is less accurate than a blood test. A veterinarian may recommend a urine test to monitor electrolyte levels in conjunction with a blood test.
Avoid exposure to toxins
Avoiding exposure to toxins is important in jaundiced dogs because the liver is responsible for removing toxins from the body. If the liver is not functioning properly, toxins can accumulate in the body, causing further damage to the liver and other organs.
Examples of toxins that should be avoided include:
- Household cleaning products: Many common household cleaning products contain toxic chemicals that can be harmful to dogs. It’s important to keep cleaning products out of reach of dogs and to thoroughly wash hands after using them.
- Pesticides: Pesticides, including insecticides, herbicides, and fungicides, can be toxic to dogs if ingested or inhaled. It’s important to keep dogs away from treated areas and to follow instructions carefully when using pesticides.
- Certain foods: Certain foods, including chocolate, caffeine, alcohol, grapes, and raisins, can be toxic to dogs. It’s important to keep these foods out of reach of dogs and to only feed them appropriately, high-quality dog food.
- Medications: Some human medications, including over-the-counter and prescription drugs, can be toxic to dogs. It’s important to keep all medications out of reach of dogs and to only give them medications prescribed by a veterinarian.
Physical activity in jaundice recovery for dogs
Physical activity plays an important role in the recovery of jaundiced dogs. Exercise helps to improve the circulation of blood, which can help to transport oxygen and nutrients to the liver. Additionally, physical activity can help to increase the release of bile, which is important for removing waste and toxins from the body.
It’s important to start with low-impact activities, such as short walks or slow play sessions, and to gradually increase the amount of exercise as the dog’s health improves. It’s also important to avoid overexertion, as this can put additional stress on the liver.
Regular exercise can also help to maintain muscle mass and strength, which can be important for overall health and well-being. It’s important to work with a veterinarian to develop a safe and effective exercise plan that is tailored to the individual needs of the jaundiced dog.
Option of liver transplant in severe cases
Liver transplantation may be considered in severe cases of jaundice in dogs. This procedure involves removing the damaged liver and replacing it with a healthy liver from a donor.
Liver transplantation is typically only recommended in cases where other treatments have not been effective or when the liver damage is so severe that it is unlikely to recover. The decision to proceed with a liver transplant is based on a variety of factors, including the dog’s overall health, age, and the underlying cause of the jaundice.
Liver transplantation is a complex and expensive procedure that requires careful planning and close monitoring. The dog will need to be closely monitored during the recovery period to ensure that the new liver is functioning properly.
Is jaundice in dogs contagious?
Jaundice in dogs is not contagious. Jaundice occurs when there is an excess of bilirubin in the blood, which can be caused by a variety of factors, including liver disease, anemia, and certain infections.
Jaundice is not spread from dog to dog through contact, as it is not an infectious disease. However, some underlying causes of jaundice, such as liver disease or infections, can be contagious and spread from dog to dog through contact with contaminated bodily fluids or tissues.
Diet for jaundiced dogs: Food options for home care
A diet that is supportive of liver function can be helpful in managing jaundice in dogs. Here are some potential food options for dogs with jaundice:
- Cooked white rice: This is an easily digestible, low-fat source of carbohydrates that can help to provide energy without overloading the liver.
- Cooked lean meat: Examples include chicken, turkey, or white fish. The protein in these foods can help to support liver function and repair liver tissue.
- Cooked or steamed vegetables: Green, leafy vegetables like spinach, kale, and collard greens are especially good for dogs with liver issues, as they are high in vitamins and minerals that can help to support liver function.
- Probiotic-rich foods: Foods like yogurt, kefir, and fermented vegetables can help to support gut health and improve digestion, which can in turn help to reduce stress on the liver.
- Omega-3 fatty acids: Fish oil and flaxseed oil are good sources of omega-3 fatty acids, which can help to reduce inflammation and improve liver function.
- Vitamin and mineral supplements: Vitamins and minerals like vitamin C, B vitamins, and iron can help to support liver function and reduce oxidative stress.
Herbal and home remedies for jaundiced dogs
While some natural remedies may have potential benefits for dogs with jaundice, it’s important to remember that not all remedies are safe or effective for all dogs. It’s always best to consult with a veterinarian before giving any home or herbal remedies to a dog. With that being said, here are some remedies that are sometimes used to support liver function in dogs:
- Milk Thistle: Milk thistle is an herbal remedy that is believed to help support liver function by improving liver cell function and reducing oxidative stress. It is available in supplements, tinctures, and teas.
- Dandelion: Dandelion is an herb that is believed to have liver-protective properties and may help to improve liver function. It is available in supplements, teas, and as an ingredient in some commercial dog foods.
- Turmeric: Turmeric is an herb that has anti-inflammatory and antioxidant properties, and may help to reduce oxidative stress in the liver. It is available in supplements, teas, and can be added to food.
- Vitamin C: Vitamin C is an antioxidant that can help to reduce oxidative stress in the liver, and may help to support liver function. Vitamin C supplements are available in various forms, including chewable tablets, liquids, and powders.
- Artichoke: Artichoke is an herb that is believed to help support liver function by improving bile flow and reducing oxidative stress. Artichoke is available in supplements and can also be fed to dogs as a food.
which vet to visit with what expertise?
It is best to visit a veterinarian who specializes in the treatment of liver diseases, also known as a gastroenterologist or a liver specialist. They have extensive knowledge and experience in diagnosing and treating liver problems in dogs, including jaundice. In severe cases, a veterinary internal medicine specialist may also be consulted. It is important to provide the veterinarian with a complete history of the dog’s health and any symptoms the dog has been exhibiting, as this will help in determining the best course of treatment.
Check out here if you are not sure about how often you should bring your dog to the vet for regular checkups.